NASA’s Psyche Spacecraft, Exploring Solar System Origins, Is Back on Track after Thrusters Lost Power
This explorer spacecraft is heading to a rare asteroid with a naked metal core. It could hold clues to how Earth began
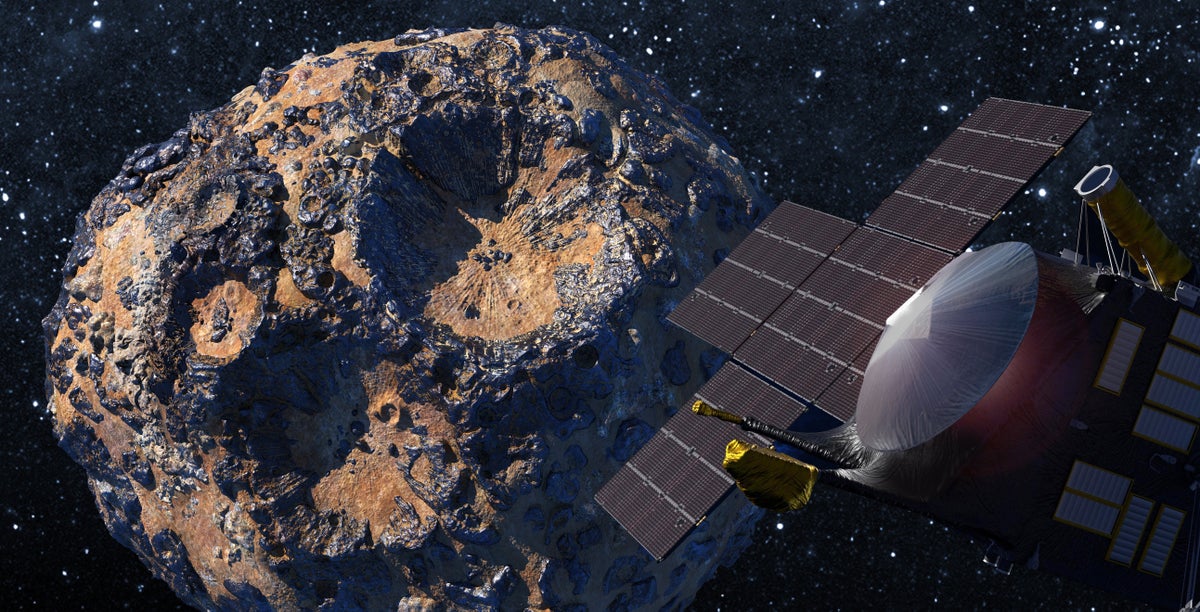
Artist rendering of the Psyche spacecraft in orbit around its namesake asteroid.
Join Our Community of Science Lovers!
The robotic spacecraft Psyche has regained propulsion after a snag cut its propellant system in April. Engineers had to switch to a backup system, and full thruster operations resumed last week. The satellite is now on schedule to fly by Mars in May 2026—and then slingshot into orbit around a very unusual asteroid (also named Psyche) in August 2029. The propulsion problem had put this schedule, and indeed the entire mission, in jeopardy for a while. “In another few weeks, if some things we tried didn’t work, the blood pressure would have started to rise,” says Linda Elkins-Tanton, the mission’s principal investigator and a planetary scientist at Arizona State University.
About 4.5 billion years ago, our solar system was a cloud of gas and dust with no planets.Astronomers used to think planets grew very slowly, over hundreds of millions of years, as gravity gradually clumped the gas and dust together. But more recent evidence points to a much faster process involving high-energy hit-and-run collisions among dust, pebbles and rocks that crashed together and then got blown apart within a short time. Some of these crashes might have melted metals to form a core (such as the one found at the center of Earth) and surrounded it with a rocky rind. Our planet’s core is many hundreds of miles deep, however—too far down to observe directly and accurately.
If you’re enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
But the asteroid Psyche, circling the sun between Mars and Jupiter, may have an exposed metal core. Radar reflections indicate this is at least partially so, says Jim Bell, an Arizona State University planetary scientist, who is in charge of the Psyche spacecraft’s multispectral imaging cameras. “If it was covered by rock, we wouldn’t get the signal that we’re seeing,” he says. That signal indicates substances composed primarily of nickel and iron. So a flyby of the asteroid could provide the first close-up view of what a planet’s core looks like and answer questions about how it formed.
The problem with the craft’s xenon gas thrusters appeared to be caused by a defective valve, and when engineers switched to a second fuel line, the craft regained motion. When Psyche meets up with its asteroid namesake in 2029, the probe’s instruments should be able to detect any uncovered core metal that collisions have blasted clean of rock. The orientation of magnetic particles in that core, like tiny compass needles, could indicate whether the asteroid once had a magnetic dynamo, as Earth’s core does. Remarkably, if there were impacts of debris on the molten metal, they could have splashed up and then frozen, leaving sharp cliffs for spacecraft cameras to show us.
The asteroid Pysche orbits at about three astronomical units, or AU, from the sun (Earth’s orbit is at one AU). It’s often described as “potato shaped,” with a diameter of 140 miles and a surface area of 64,000 square miles.
Josh Fischman is a senior editor at Scientific American who covers medicine, biology and science policy. He has written and edited about science and health for Discover, Science, Earth, and U.S. News & World Report. Follow Josh Fischman on Twitter.
Source: www.scientificamerican.com